AGA geodiemeter`s van 3 tot 8
muv AGA 6

1950 Geodimeter var från början en elektrooptiskt längdmätare uppfunnen av Erik Bergstrand
och senare utvecklad av Ragnar Schöldström på AGA.
AGA geodiemeter 3
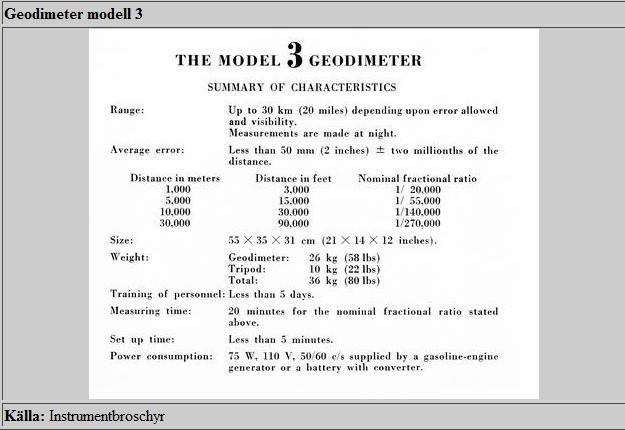

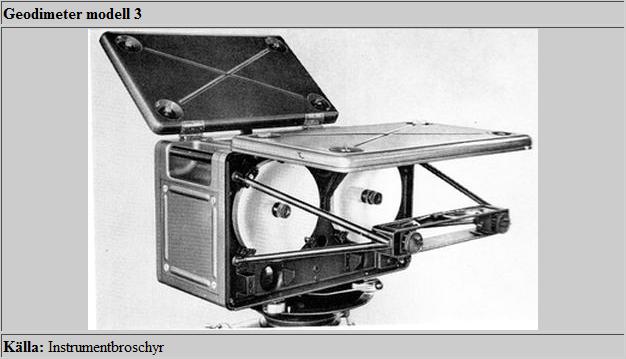

AGA Geodetic Distance Meter 1956.



Prisme produsert av firmaet AGA i Sverige
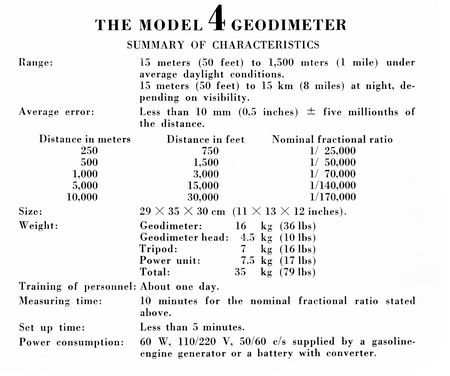
AGA geodiemeter 4

AGA Geodimeter modell 4 1967


AGA Geodimeter modell 4 1967

Eigendom AGA museum, gekregen uit Engeland
AGA Geodimeter modell 4 1967
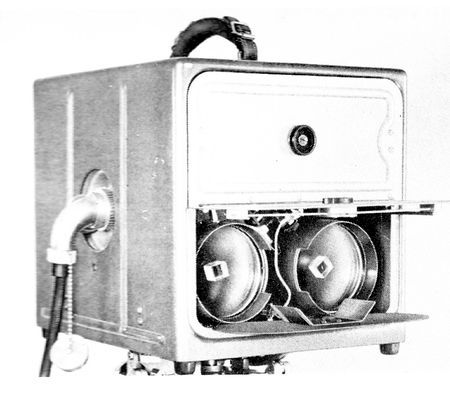


AGA Geodimeter modell 4 1967

AGA Geodimeter modell 4 1967
Hauptmodulationsfrequenz 30 MHz, Strahlungsquelle: 3 x 30W-Hg-Lampe
Geodätisches Institut der Leibniz Universität Hannover 3 ca. 1958
Strahlungsquelle: 3 x 30W Hg Lampe Kerrzelle, Reichweite Tag 1,5 km, Nacht 15 km Genauigkeit +/-(1 cm +2 x 10-6 x D)
AGA wurde 1947 in Stockholm gegründet.
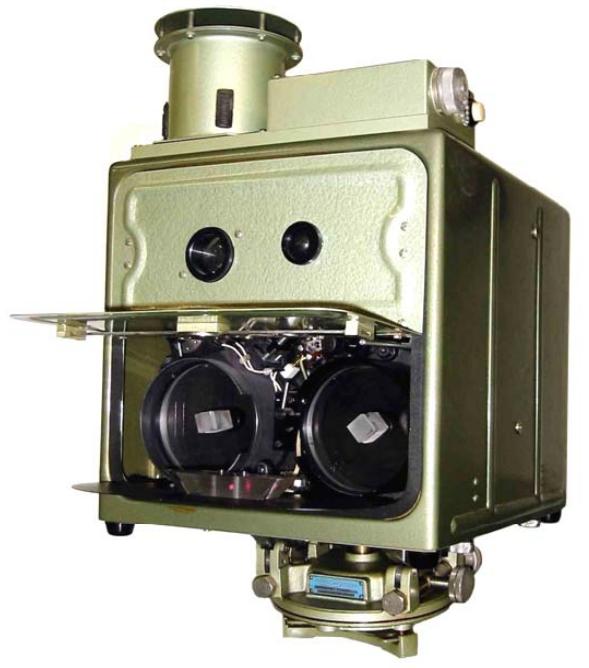

AGA Geodimeter modell 4
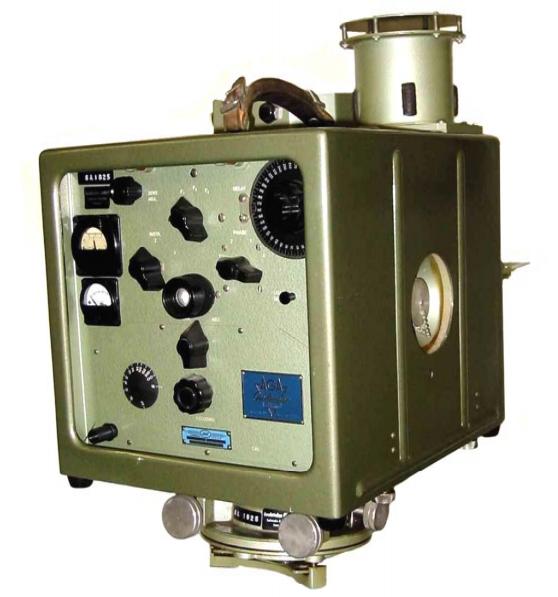

AGA Geodimeter modell 4b
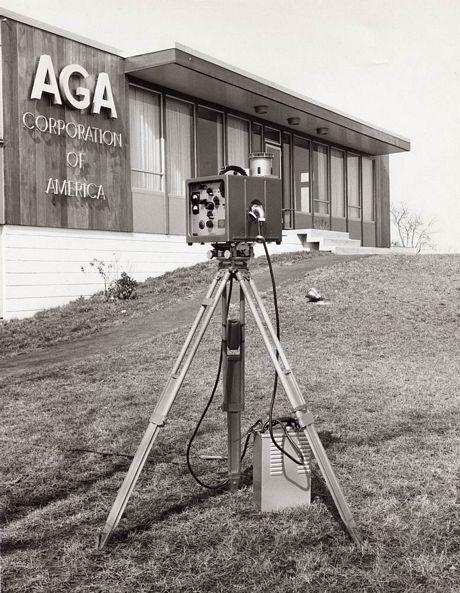



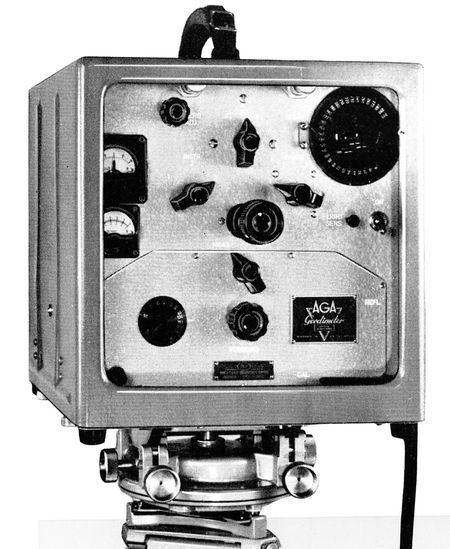
Geodimeters, first developed in the 1950s, evolved quickly in the 1960s. In the “4 series” (shown in the photo), weight was scaled down to 20 pounds and measuring time was reduced from 45 minutes to 10 minutes, compared to earlier Geodimeter models.
For lightwave instruments, a complete set of measurements consisted of four separate observations: two measurements with the prism over true center, then measurements with offsets of 0.4 meters. Two complete sets of these measurements, separated by 24 hours, were made. Accuracy of the measurements could be affected by optics alignment, frequency drift, and calibration curve errors in the phase readings. Wet and dry bulb thermometer readings were taken at one end of the line and temperature and pressure readings were taken at both ends of the line both before and after measurements. Altimeter readings were also taken.
The 4D used a high-pressure mercury vapor lamp rather than a common tungsten light bulb as its light source. First manufactured in 1963, the “D” in its designation indicated that it could be used in daylight. The Coast and Geodetic Survey (C&GS) used this model throughout the 1960s.
In 1966, the 4D was modified to use a laser as its light source, in order to increase its range in moderate haze and to measure longer distances in bright sunlight. C&GS technician George Lesley replaced the mercury vapor lamp with a three-milliwatt helium-neon gas laser. The modified 4D was designated “4L,” and replaced the 2A and 4D models on the Transcontinental Traverse. Later, the three-milliwatt laser was replaced with a six-milliwatt laser and the model was renamed “4L 6A.”
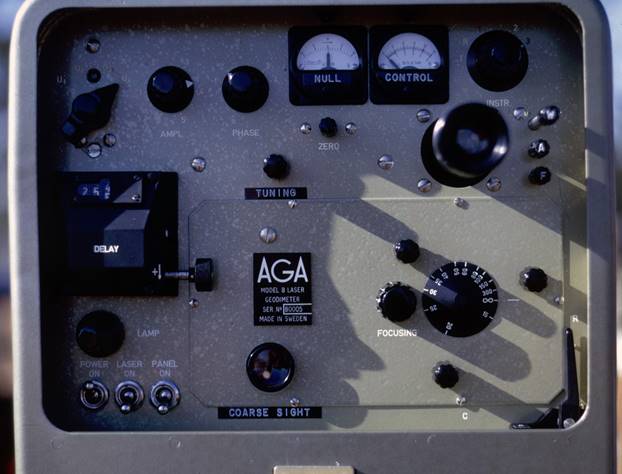















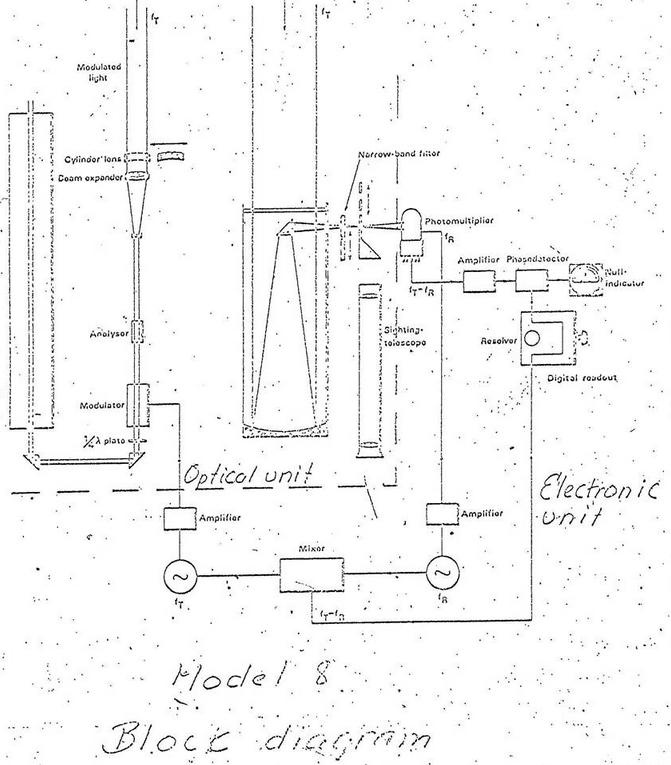
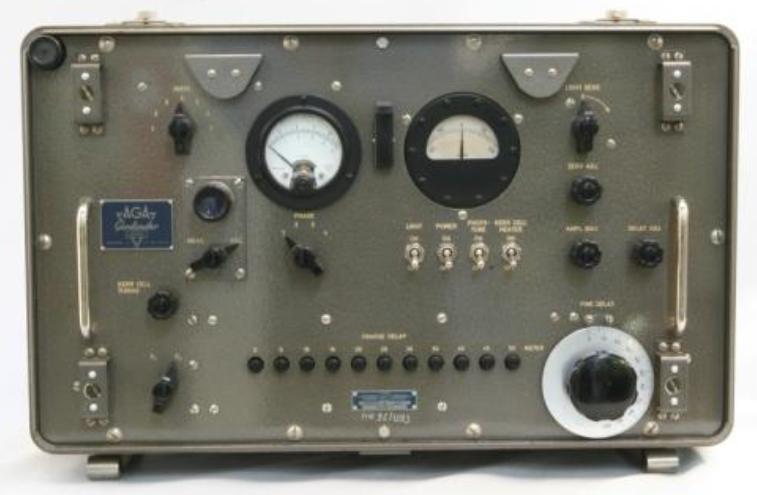
AGA-1969-8




AGA Geodimeter modell 8
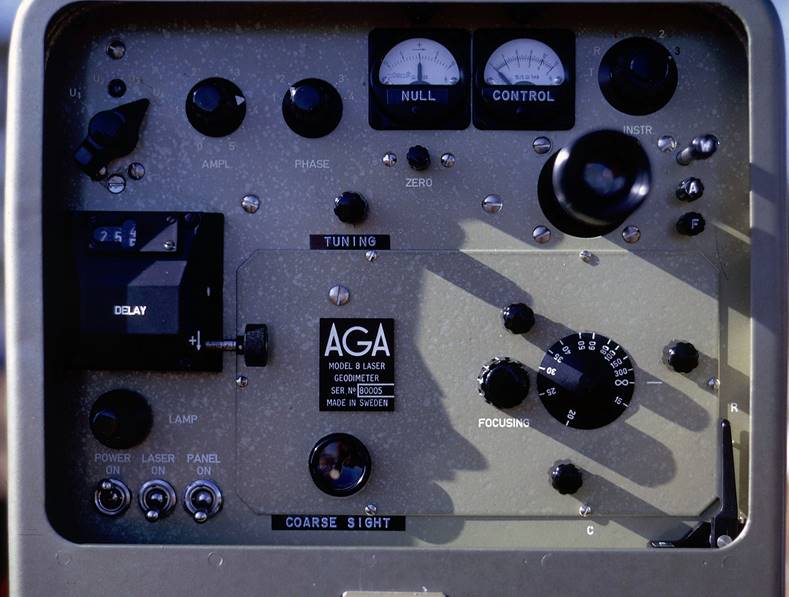


AGA Geodimeter modell 8